Find out more about krill, a small, shrimp-like crustacean found throughout the world’s ocean. Find out which krill are sustainable and where to buy sustainable krill.
What are krill?
Antarctic krill are small, shrimp-like crustaceans found in dense swarms in the Southern Ocean. They are a vital species in the food chain, so must only be fished in a sustainable way.
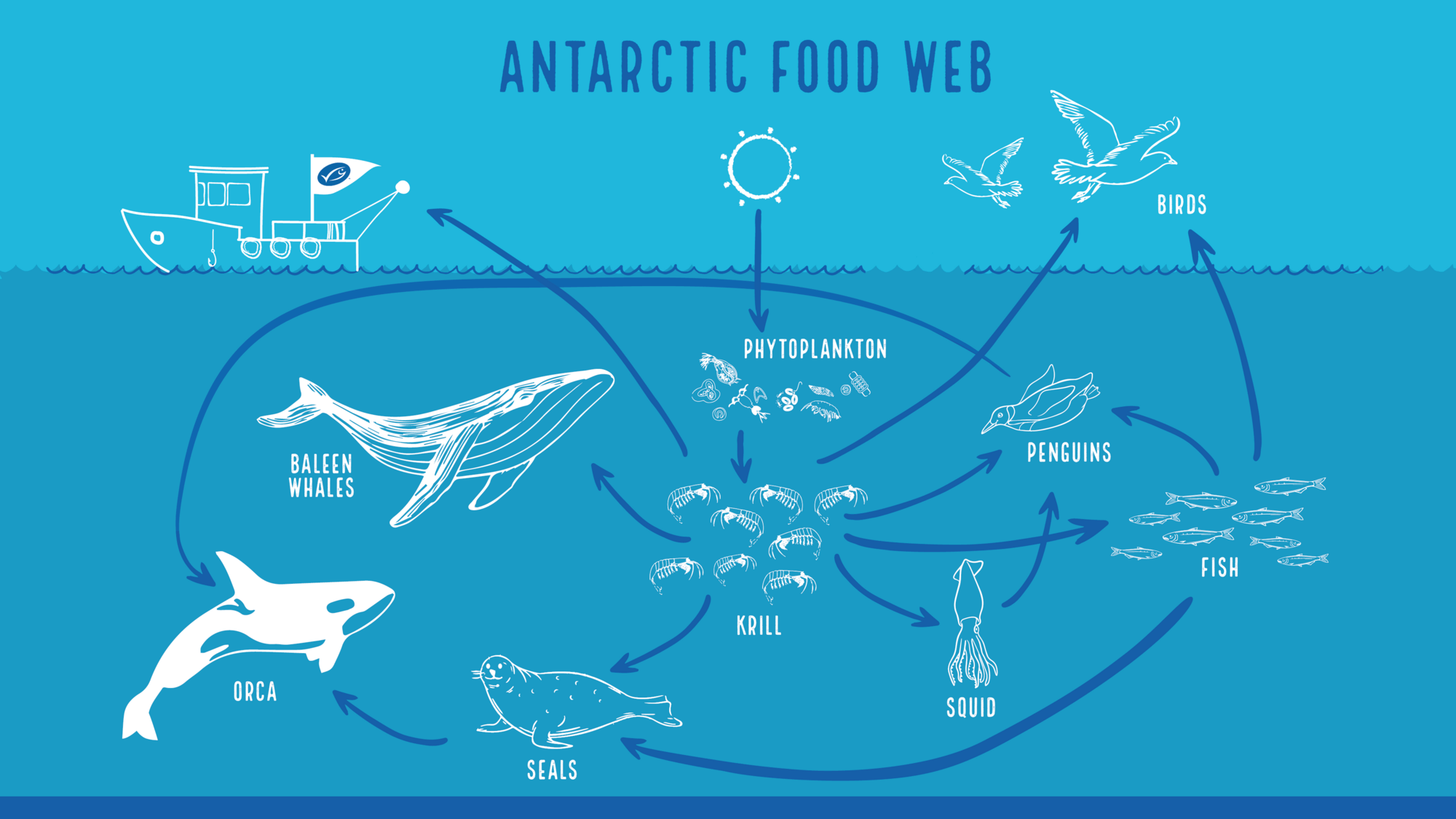
Many species within the Antarctic ecosystem depend on krill for survival. They are the primary source of food for whales, seals, penguins and other marine species.
Krill are a keystone species meaning that if they are removed from the food web, it could lead to its collapse, therefore their fishing must be managed sustainably.
Krill facts
Antarctic krill are a vital part of the wider ecosystem for that ocean.
Krill are a small crustacean and a keystone species in the Antarctic ecosystem since they serve as food for whales, seals, penguins and other species. It is therefore essential that krill fishing is conducted in a sustainable way, informed by science and research.
Krill are rich in Omega-3 phospholipids and the naturally occurring antioxidant Astaxanthin.
Krill are processed to form krill oil, sold as a liquid or in capsules for their health benefits. Krill meal and oil are also used in aquaculture and animal feed.
Fishing in the Antarctic is regulated by the Commission of Antarctic Marine Living Resource (CCAMLR). CCAMLR is a legally binding international convention among 27 Members and 10 Acceding States to ensure the conservation of the Antarctic ecosystems.
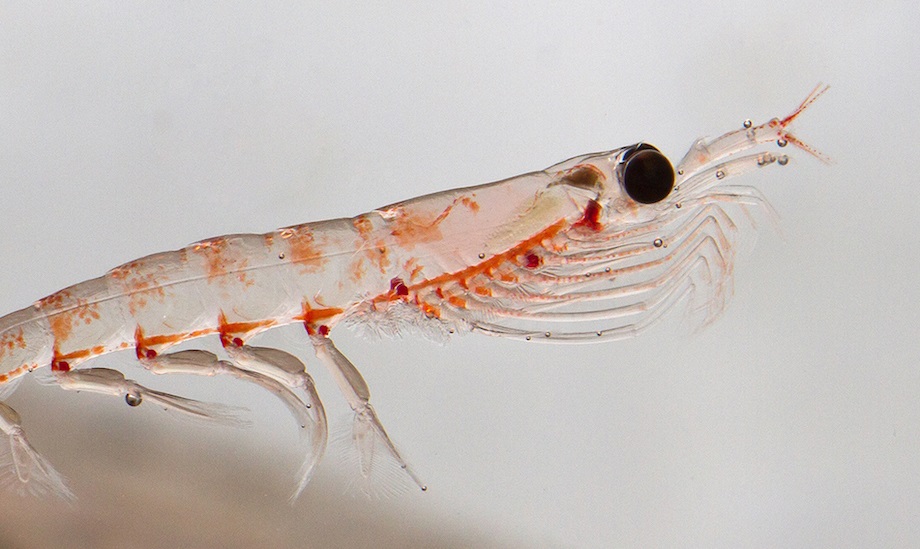

Why are krill harvested?
Krill are rich in Omega-3 fats and the naturally occurring antioxidant Astaxanthin. They are processed to form oil and sold as a nutritional supplement in liquid or capsule form. Krill meal and oil are also used in aquaculture and animal feed.
The market for krill oil is growing and so krill fisheries need to be well-managed. Fishing should be informed by science and research and closely monitored to ensure it is sustainable.
Are krill sustainable?
There is no such thing as a sustainable species of fish. Only sustainable populations of fish.
Fishing for krill can be done sustainably by fisheries certified to the MSC Fisheries Standard.
Where can I buy sustainable Krill Oil?

Krill oil products carrying the MSC blue fish tick are certified sustainable.
MSC-labelled krill oil comes from a wild-capture fishery that has been independently assessed to the MSC Fisheries Standard.
Companies using the blue fish tick throughout the supply chain have been assessed to ensure products can be traced back to an MSC-certified fishery.
How can we be sure that krill populations are well-managed?
Fishing in the Antarctic is regulated by the Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resource (CCAMLR).
A legally binding international convention to ensure the conservation of the Antarctic ecosystems was established in 1982. CCAMLR has 27 members and a further 10 countries have agreed to the convention.
The commission takes a cautious approach to fishery management. Recognising the need to protect krill populations, CCAMLR set a ‘trigger catch limit’ of 620,000 tonnes, which is 1% of the total estimated biomass.
Over the past decade, krill catch has been increasing, though it remains below the trigger catch limit.
Climate change and other environmental effects may also have an impact on krill populations. That is why is it important for krill fisheries to be managed at their current precautionary levels, keeping catch low.

Learn more about sustainable krill fishing
Antarctic krill fisheries certified to the MSC Fisheries Standard undergo stringent management through independent assessment, evaluation, and monitoring. These certified fisheries demonstrate a strong commitment to sustainability by investing in scientific research, gear innovation, and international cooperation under the Antarctic governance structure.
As a result, they rank among the world’s top-performing fisheries for environmental sustainability.
The MSC Fisheries Standard is the leading global benchmark for sustainable fishing. It assesses whether a fishery is well-managed and environmentally responsible and is the only international wild-capture certification program meeting best practice requirements set by the UN Food and Agriculture Organization, the Global Sustainable Seafood Initiative (GSSI), and the ISEAL Alliance.
MSC certification is voluntary, and certified fisheries undergo independent, regular audits by accredited Conformity Assessment Bodies (CABs) to ensure adherence to best practices.
Does krill fishing threaten Antarctic wildlife such as penguins and whales?
Founded in 2012, the Association of Responsible Krill harvesting companies (ARK) is a group of eight krill fishing companies from four CCAMLR member countries (Norway, the Republic of South Korea, Chile, and China).
The total fishing capacity of ARK members represents over 90% of all krill catches in CCAMLR waters.
ARK fisheries take voluntary steps to help protect Antarctic wildlife. These measures go beyond the requirements of CCAMLR directives and support their ability that meet or exceed the MSC Fisheries Standard.
Krill fishing and penguins
To mitigate the impacts of krill fishing on penguin colonies, fishing industry partners, represented by ARK in collaboration with WWF, have implemented a voluntary seasonal buffer zone of 4,500 km2 – the equivalent of over 84,000 football fields.
This seasonal buffer zone encompasses the foraging and chick-rearing areas for over 74% of chinstrap, almost 98% of Gentoo, and above 91% of Adélie penguin colonies, offering significant protection to most penguins around krill fisheries.
Further year-round voluntary closures around the Antarctic peninsula provide additional protection for penguin colonies during their breeding seasons.
Krill fishing and whales
ARK have implemented the use of seal exclusion devices on their vessels. In a direct and timely response to scientific observer findings of three whale mortalities in the 2020/2021 season, participating vessels adapted these exclusion devices also to exclude whales from the trawl mouth.
Since the whale exclusion devices were fitted, no further whale incidents have been recorded, and the innovation is expected to be adopted industry-wide.
Krill fishing innovation
Furthermore, ARK fishing vessels use eco-harvesting techniques by keeping fishing nets underwater for longer, reducing energy consumption. The technique also benefits seabirds by avoiding repeated casting and retrieval of fishing gear, the risk of unintentional interactions is lessened.
Overall, because of CCAMLR, the MSC and ARK management systems, Antarctic krill fisheries operating within all three programs rate among the most environmentally sustainable and well-regulated fishing operations on the planet.
Explore more sustainable fish to eat
Find more sustainable seafood species that are MSC certified in Australia and New Zealand.
Explore the sustainable seafood guide.

Sustainable seafood recipes
Chefs and seafood lovers from around the world share quick and tasty ways of cooking MSC certified seafood.

10 reasons to choose the blue fish tick
Choose seafood which helps to protect oceans, livelihoods and fish for the future.

Buy sustainable seafood
Where to find the blue fish tick at supermarkets, fish shops and restaurants.

