Is seafood caught through purse seine fishing sustainable? Find out more about this method of fishing and how its impact on the ocean can be reduced.
What is purse seine fishing?
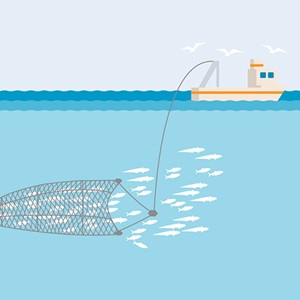
Purse seine fishing takes place in the open ocean, using a large net - the purse seine - to target dense schools of single-species pelagic (midwater) fish like tuna and mackerel.
How does purse seine fishing work?
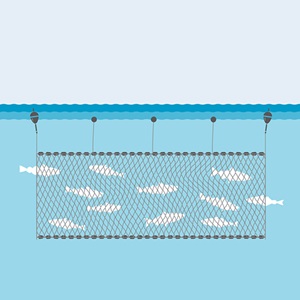
A seine net is suspended like a curtain from the ocean surface with floats along its top edge and a weighted rope threaded through the bottom.
When a school of fish is found, a small boat will lead the net in a circle so the curtain surrounds the school. Once encircled, the bottom rope on the net is drawn tight to snare the fish and prevent them from escaping. This drawing shut of the seine is like tightening the cords of a drawstring purse, hence the name.
A purse seine net can be more than 2000 metres in length and reach around 200 metres in depth. The size can vary depending on the vessel they are deployed from, the size of the mesh, and the target species.
/rs5081_purse-seine-copy-body.tmb-large1920.png?Status=Master&Culture=en&sfvrsn=f2edd296_1)
What species are caught by purse seines?
Purse seines are used for schooling pelagic fish species of various sizes. Pelagic fish are those that swim in the water column of the open ocean, up to approximately 200 metres depth.
Species caught using purse seines include anchovies, sardines, mackerel, squid and tunas. In 2022 approximately 67.5% of the world’s tropical tuna species (skipjack, bigeye and yellowfin) were caught by purse seine fishing vessels.
Fish Aggregating Devices (FADs)
Purse seine fishers frequently use Fish Aggregating Devices (FADs) to find their catch.
FADs are man-made floating objects that attract fish and can be either drifting or anchored. FADs are equipped with geolocating equipment and sonar to find their target species. They increase the efficiency of the fishing operation and reduce uncertainty around catch volumes.What are the environmental impacts of purse seine fishing?
All types of fishing gear can have an impact on the ocean environment and can have significant environmental impacts, if not sustainably managed.
Bycatch
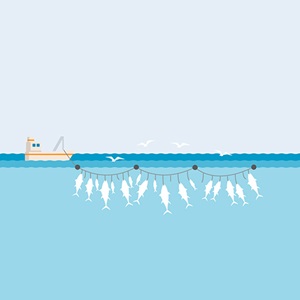
The overall size of the net means anything within its confines can be caught as bycatch. Bycatch includes any undersized fish, non-target species, and Endangered, Threatened and Protected (ETP) species.
When associated with FADs, the risk of bycatch in purse seine fishing can increase. This is because some FADs include long (up to 50 metres) appendages that can entangle non-target species.
The volume and type of species present in bycatch varies depending on whether the purse seine net is set around a free school of tuna, a drifting FAD, or an anchored FAD.
Habitats
As purse seines make no contact with the seabed and are set in open water, the nets direct impact on habitats is generally considered to be low.
However, FADs are frequently made of non-biodegradable materials and are often lost at sea. Lost or discarded FADs become 'ghost gear', polluting and littering the ocean while continuing to trap and catch marine animals long after it has been abandoned.
The Decision film
How can purse seine fishing prevent overfishing?
Fisheries certified as sustainable to the MSC Fisheries Standard must ensure their fishing operations are targeting stocks that are scientifically verified as abundant i.e. there are enough mature individuals left to reproduce and replenish the stock.
To prevent overfishing sustainable purse seine fisheries have made alterations to the depth and size of their nets and their setting techniques. These modifications help reduce bycatch and wasteful discards.
How can purse seine fishing prevent bycatch?
Sustainable fisheries are often required to make improvements to their operations and modify their gear to reduce their interactions with non-target species and minimise bycatch.
Sustainable purse seine FAD fisheries do not use entangling nets on their FADS. This helps reduce the amount of ETP species accidentally caught by FADs.
Improvements can also include onboard modifications like secondary chutes to release sharks. Additionally, many sustainable purse seine fisheries voluntarily engage in tag-and-release programs. This contributes to the scientific knowledge of ETP species' life histories and movements so that future interactions can be minimised.
How MSC Certified fisheries are improving
How can purse seine fishing reduce its environmental impacts?
MSC certified fisheries must demonstrate they are minimising their impacts on marine ecosystems, habitats and ETP species.
In the case of FAD-associated purse seine fishing, this includes using more biodegradable and non-entangling materials in the construction of FADs. If lost or discarded, biodegradable FADs will eventually disintegrate naturally and not cause plastic pollution or act as ghost gear.